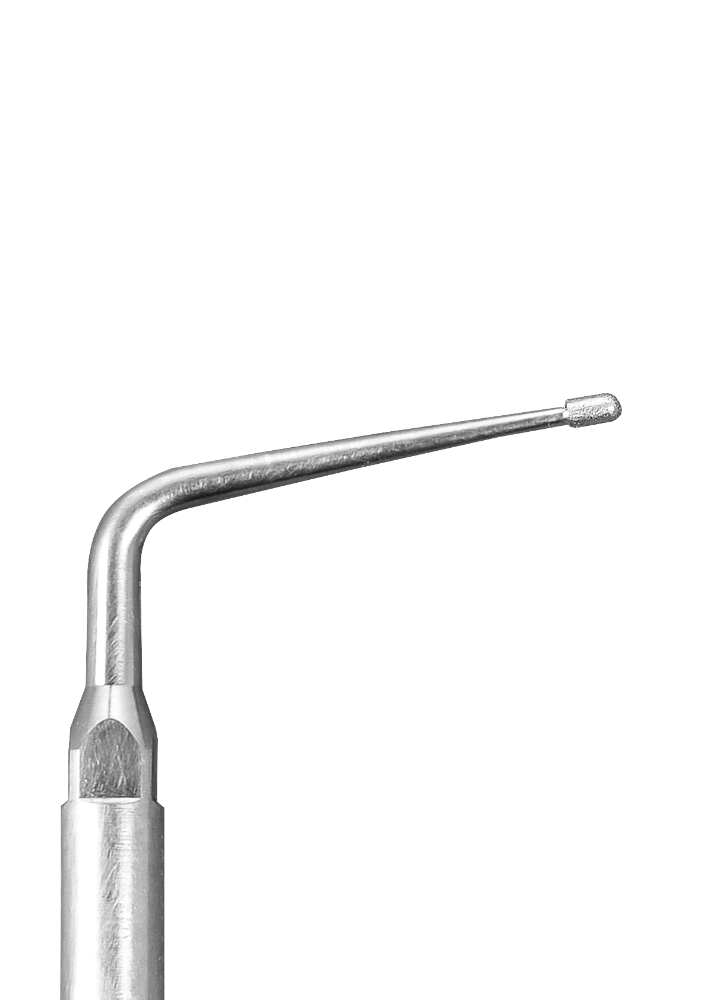
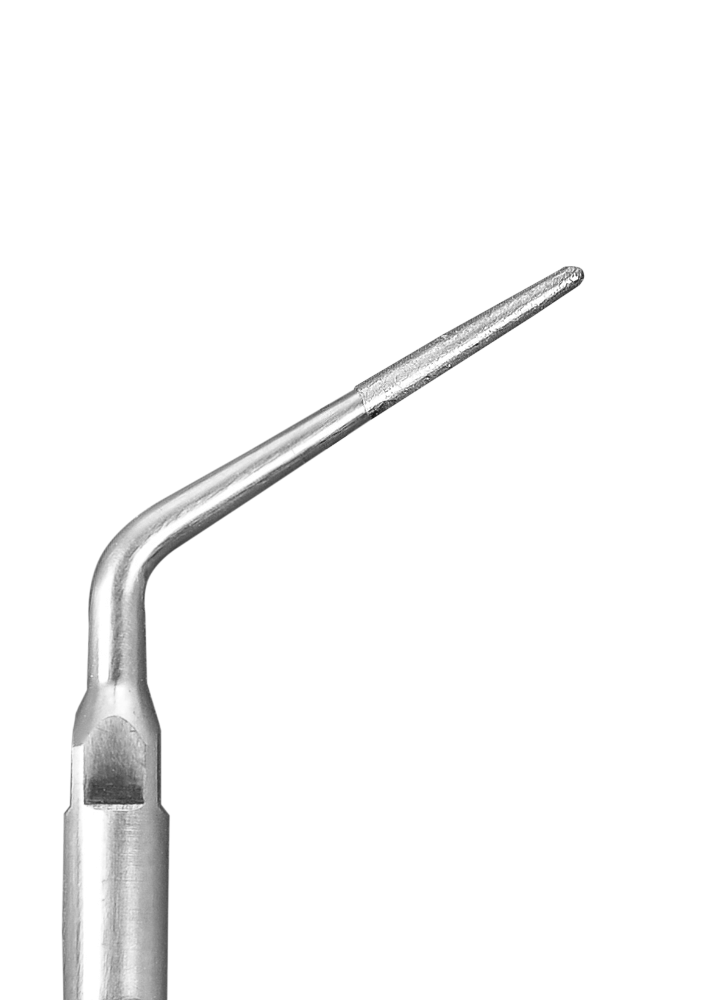
Locating Calcified Canals
Fast and safe removal of blockages.
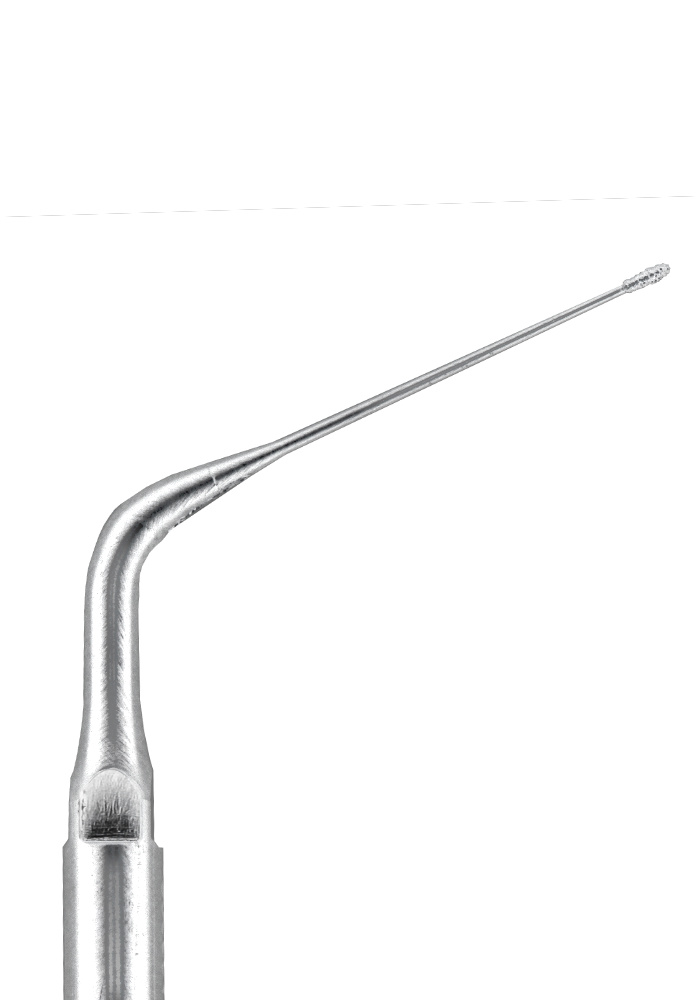
One of the challenges in endodontics is the removal of calcifications that block the access to the root canals. The best treatment for this condition is the combination of magnification and ultrasonics. The improved visualization and the conservative removal of tooth structure with the ultrasonic tip result in fewer iatrogenic errors.
Knowing where to access is only the first step.
1st Law of canal location
The root canal access is always located in the floor-wall junction (FWJ).
2nd law of canal location
The root canal access is always located in a vertex.
Step-by-Step Calcified Canal Location
2. Initiate the removal through straight and continuous movements over the calcification (do not use water during this step).
3. Ultrasonic inserts are meant to be used for short periods of time, to avoid overheating. To rinse and remove dentin and pulp remains, use a syringe containing sodium hypochlorite, followed by suction and drying of the pulp chamber.
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until all obstructions are eliminated
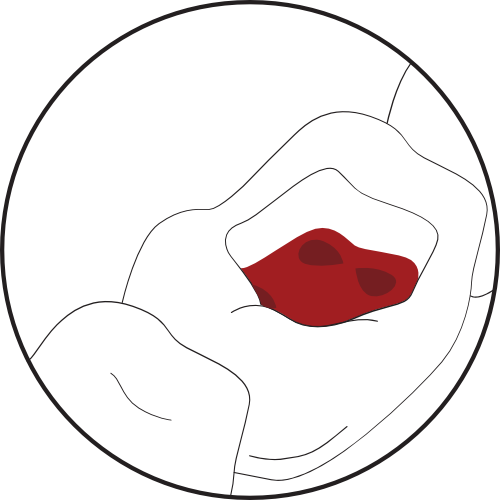 1. Pulp chamber with calcifications obstructing the access to the canals.
1. Pulp chamber with calcifications obstructing the access to the canals.
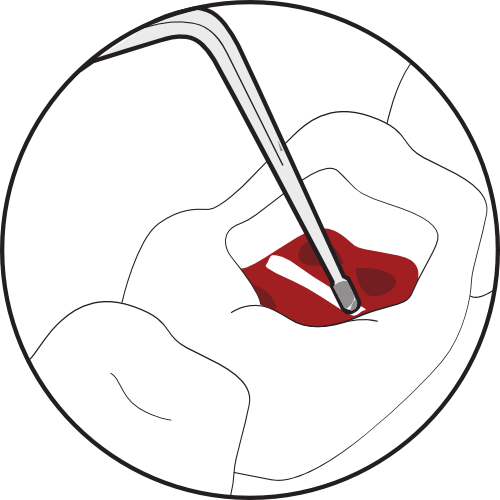
2. Ultrasonic tip in contact with calcification and activated to remove obstructions.
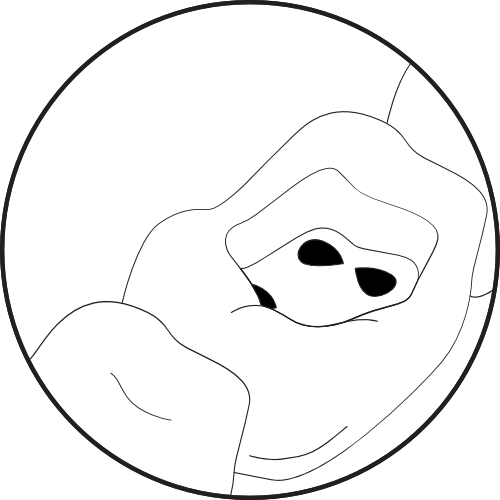
3. Accessible canals after instrumentation with ultrasonic insert.
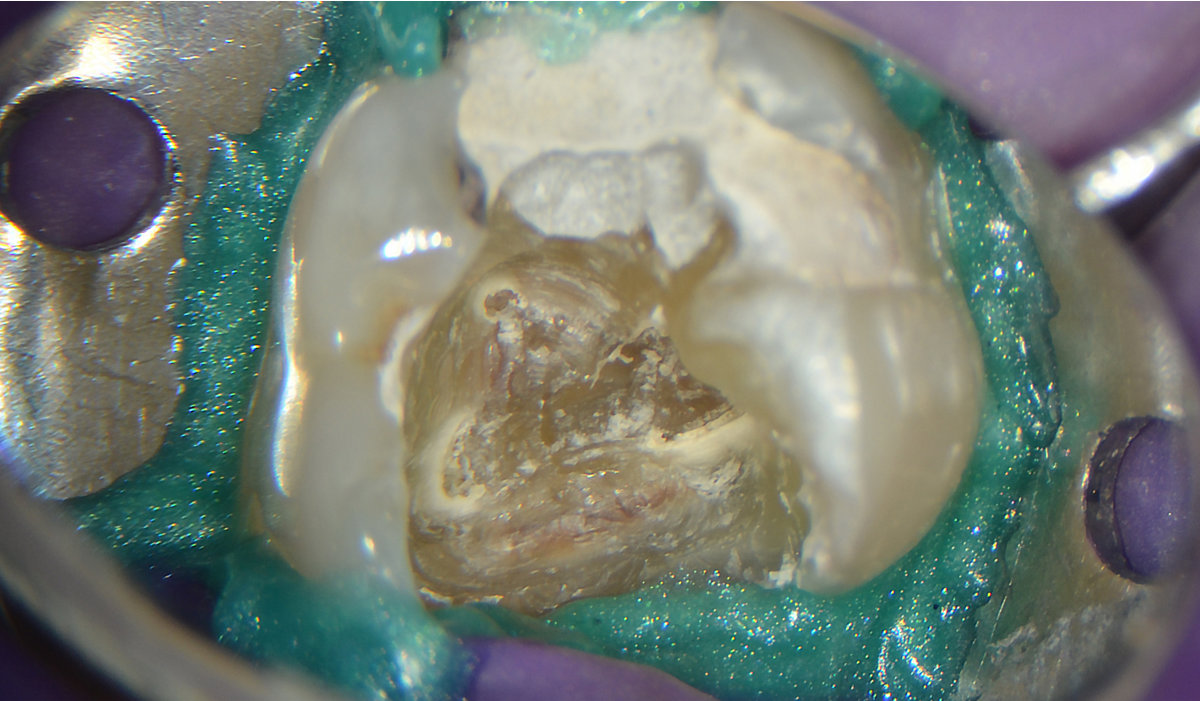
Pulp chamber with calcifications obstructing the access to the canals.
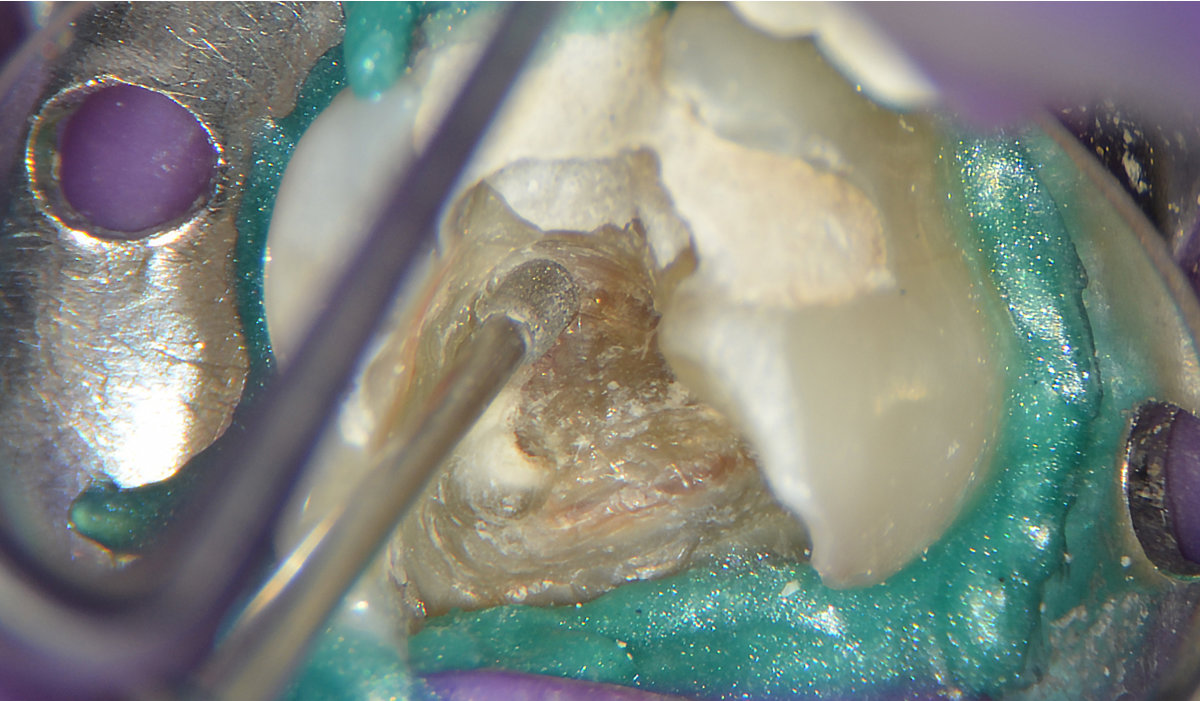
E6D ultrasonic tip activated in contact with calcifications.
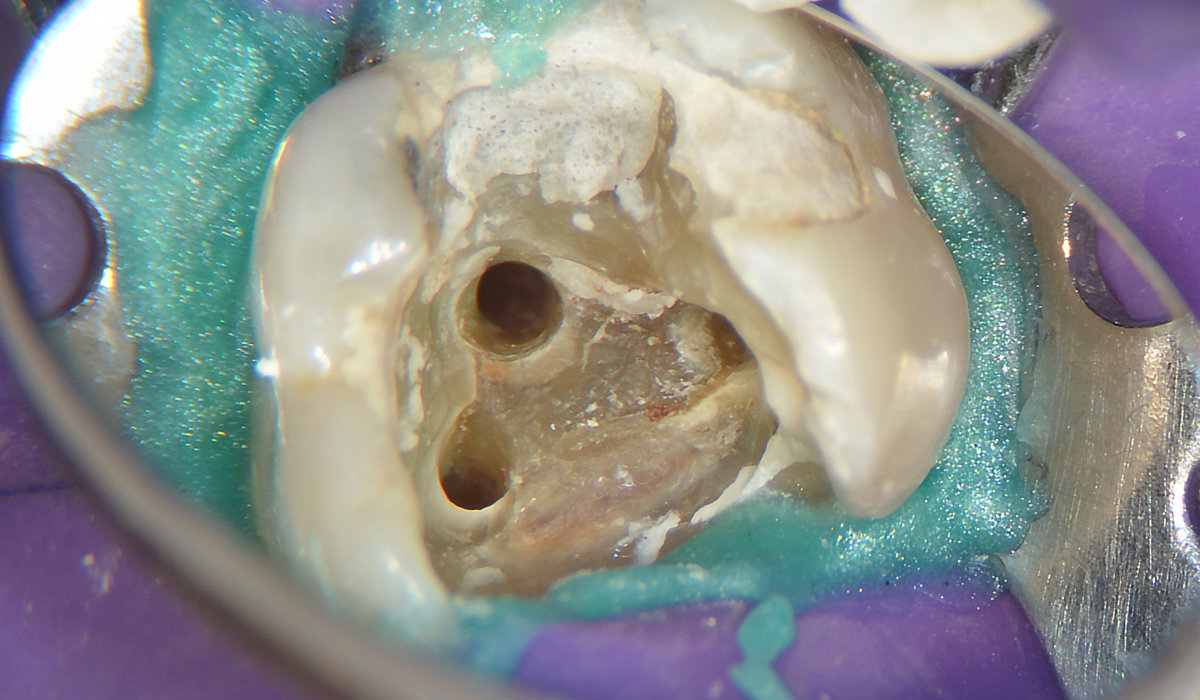
Accessible canals after instrumentation with ultrasonic insert.